Traceability
In safety-critical designs, requirements are the source of all design and verification activities. Moreover, the relationships between the requirements and all other projects artifacts allow for the tracking, management and demonstration of strict requirements-based design and verification processes being followed. Such relationships are called traceability data.
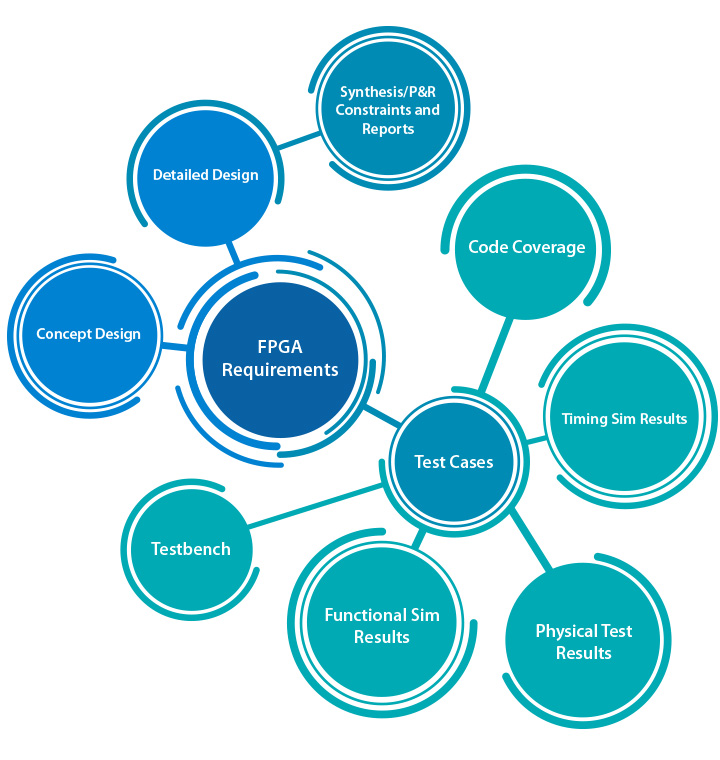
Figure 1. Relationships between requirements and other project artifacts.
Traceability Matrices
A traceability matrix is a spreadsheet showing the correlation between pairs of project artifacts. The most common matrices created during the hardware designs show the relationships between:
- Circuit Card Assembly and FPGA requirements
- FPGA requirements and test cases
- Test cases, testbench and verification results
- FPGA requirements, conceptual and detail design
Traceability matrices demonstrate the completeness of the project at each level: requirements, design, and verification. The matrix in top-down direction (downstream traceability) confirms all the requirements are allocated, implemented, and verified, while a bottom-up view (upstream traceability) reveals unused elements and the opportunity to discover potential gaps and errors in the traceability data.
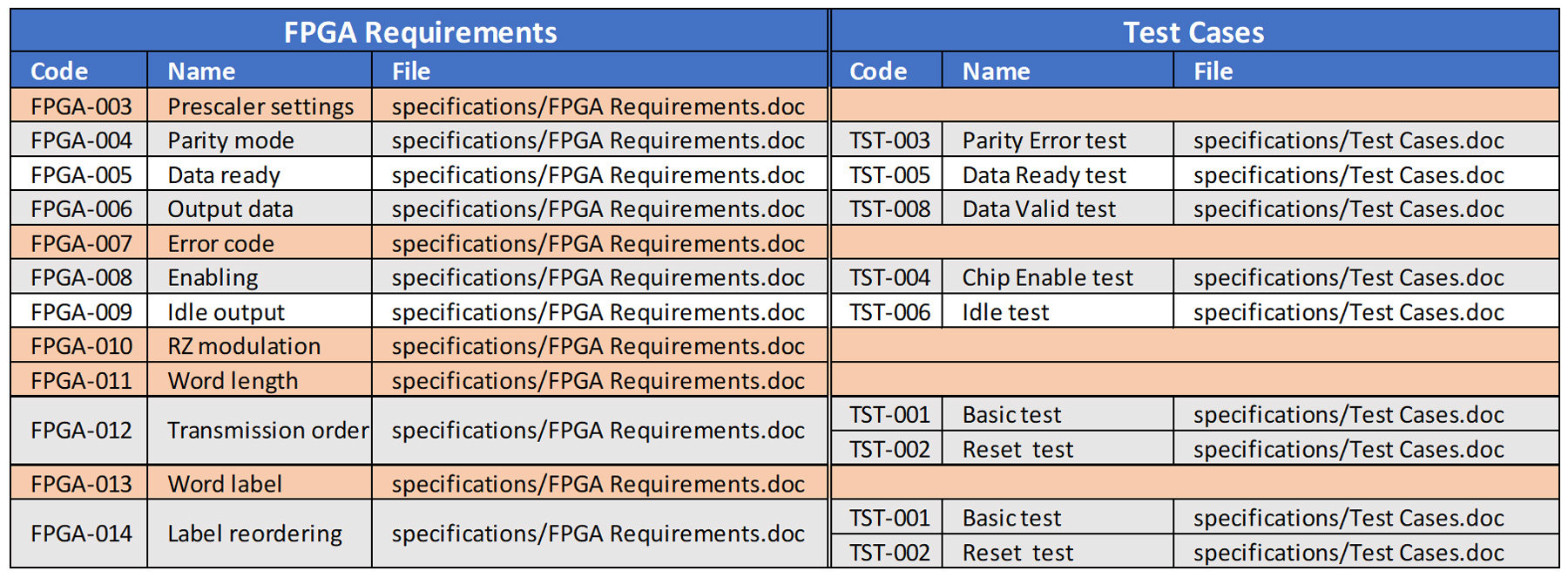
Figure 2. Relationships between FPGA Requirements and Test Cases in top-down direction.
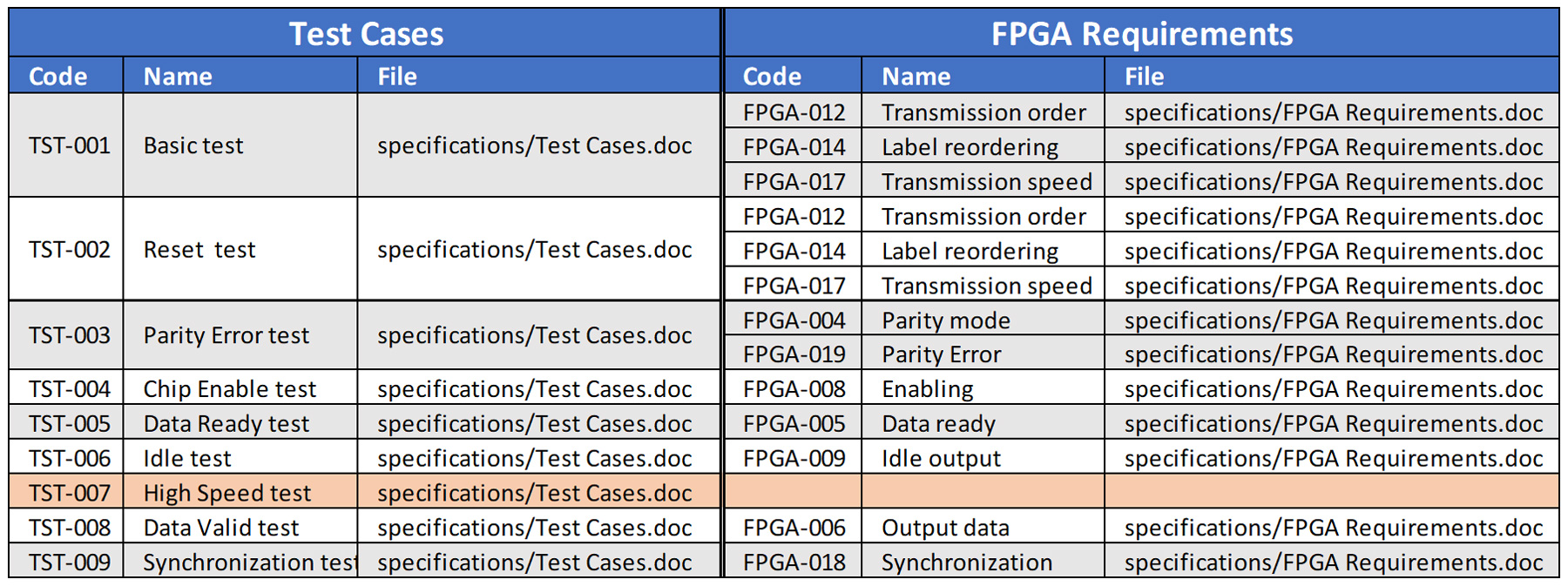
Figure 3. Relationships between FPGA Requirements and Test Cases in bottom-up direction.
Change Impact Analysis
Requirements changes are a part of the development cycle and if they are not properly controlled, they may seriously impact the safety of the final product. Properly created and maintained, traceability matrices are crucial for the change management process.
Spec-TRACER™
Aldec's Spec-TRACER tool, available within Active-HDL, streamlines the traceability capture and analysis process ensuring that each requirement has been fully implemented, covered, and verified. Requirements coverage gaps as well as unused HDL functions are easily exposed and reported using multi-directional traceability matrices.
Corporate Headquarters
2260 Corporate Circle
Henderson, NV 89074 USA
Tel: +1 702 990 4400
Fax: +1 702 990 4414
https://www.aldec.com
©2026 Aldec, Inc.
